Aida Controller & Platform Architecture
Overview
The Aida system is a distributed building management solution composed of two main components:
- Aida Controller: An on-premises, Dockerized server deployed at each site/building, responsible for local automation, device integration, and data aggregation.
- Aida Platform: A cloud-based application that manages multiple controllers/sites, provides centralized analytics, and exposes APIs for third-party integrations.
This architecture ensures robust local operation at each site, while enabling centralized management, analytics, and integration at the platform level.
High-Level Architecture Diagram
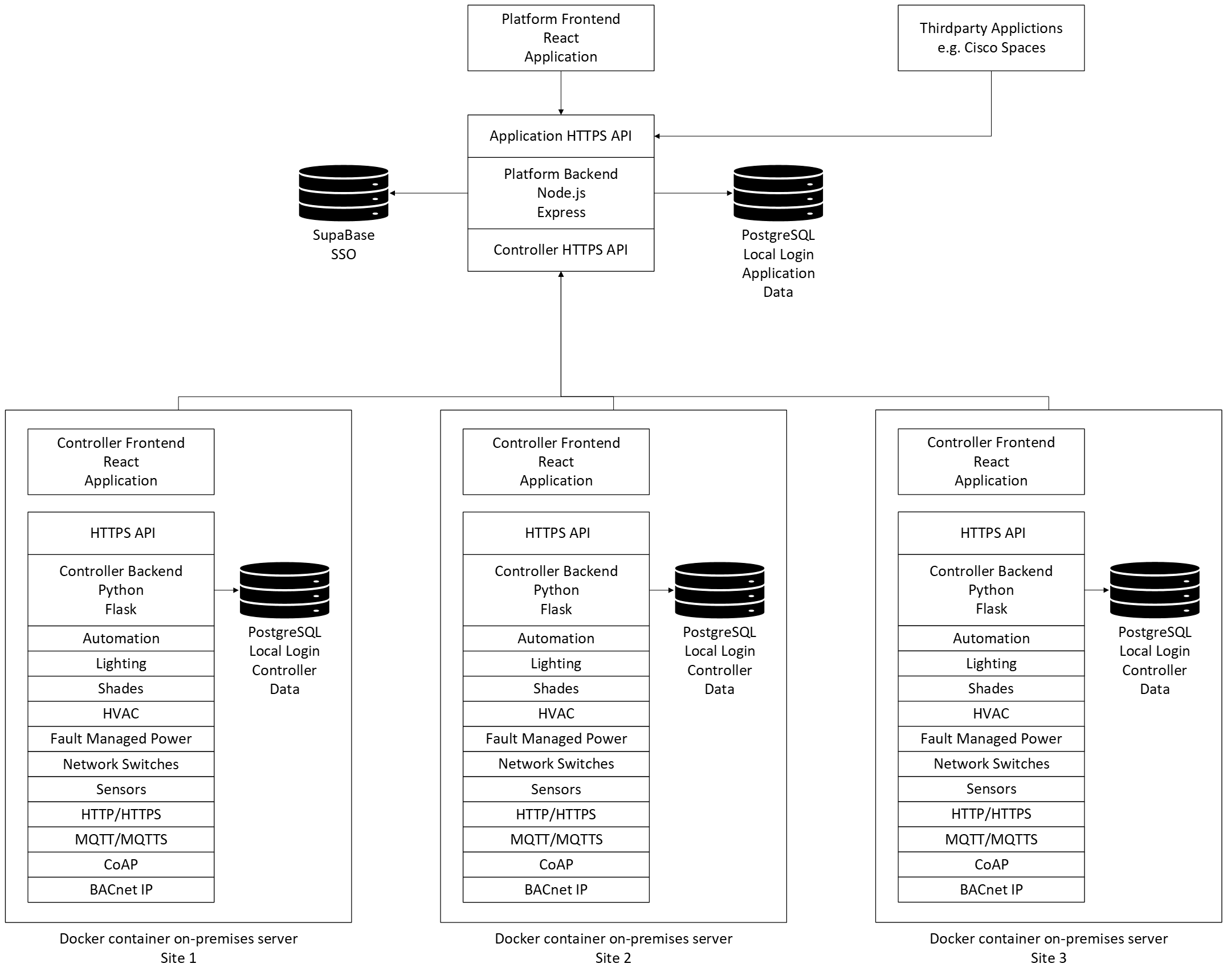
Components
1. Aida Platform (Cloud)
- Platform Frontend:
- Built with React.
- Provides a unified dashboard for managing all sites and controllers.
- Platform Backend:
- Built with Node.js and Express.
- Exposes an HTTPS API for the frontend, controllers, and third-party applications.
- Handles authentication (via SupaBase SSO), user management, and site aggregation.
- Database:
- PostgreSQL for application data, user accounts, and site metadata.
- Third-Party Integrations:
- External applications (e.g., Cisco Spaces) can interact with the platform via the HTTPS API.
2. Aida Controller (On-Premises, Per Site)
Each site runs its own Aida Controller instance in a Docker container, providing:
- Controller Frontend:
- React-based local dashboard for configuration and monitoring.
- Supports local login.
- Controller Backend:
- Python (Flask) application.
- Exposes an HTTPS API for the frontend and for secure communication with the platform.
- Handles all automation logic and device integrations.
- Local Database:
- PostgreSQL for storing site-specific data, configuration, and local user accounts.
- Automation Modules:
- Lighting Control & Automation
- Shade Control & Automation
- Fault Managed Power (FMP) Control & Automation
- HVAC Control & Automation
- Sensor Data Collection
- Protocol Support:
- HTTP/HTTPS
- MQTT/MQTTS
- CoAP
- BACnet IP
- Device Integration:
- Network switches, sensors, and other building management devices.
Data Flow
-
Local Operation:
- Each controller operates autonomously, managing devices and automation at its site.
- Local users can access the controller dashboard for configuration and monitoring.
-
Platform Integration:
- Controllers communicate with the platform backend via secure HTTPS APIs.
- The platform aggregates data from all controllers for centralized management, analytics, and reporting.
-
Authentication:
- Platform users authenticate via SupaBase SSO.
- Controllers support local login for on-site access.
-
Third-Party Access:
- External applications can access platform data and features via the platform's HTTPS API.
Deployment Model
-
Controllers:
- Deployed as Docker containers on-premises at each site.
- Each controller is independent, ensuring local resilience and operation even if cloud connectivity is lost.
-
Platform:
- Deployed in the cloud, managing multiple controllers/sites.
- Provides a single pane of glass for enterprise-wide building management.
Security Considerations
- All API communications use HTTPS for secure data transfer.
- Platform authentication is managed via SupaBase SSO.
- Controllers support local authentication for on-premises access.
- Data segregation between sites is enforced at both the controller and platform levels.
Scalability
- The architecture supports scaling to hundreds or thousands of sites, with each controller operating independently.
- The platform backend and database can be horizontally scaled to handle increased load and data volume.
Summary
The Aida architecture provides a robust, scalable, and secure solution for modern building management, combining the reliability of on-premises control with the power and flexibility of cloud-based management and analytics.